IT Tools is a free, open-source, self-hosted web service that provides handy utilities for developers and IT folks. From now on I'll include both a docker-compose.yml and a simple Kubernetes manifest for each service I cover.
Tested with
- Single host or Raspberry Pi
- Docker / Docker Compose or K3s
Prerequisites
- A host to run the servicer (server, VM or PI)
- Docker (with docker-compose) or a Kubernetes clister (K3s, microk8s, etc.)
Quick notes
- The app listens on container port 80. The examples below expose it as host port 9080 (Docker) or NodePort 31080 (Kubernetes). Change those to fit your network.
- If you run multiple services on one node, prefer an Ingress controller (and TLS) over NodePorts.
Installation
IT Tools is distributed as a container, so as every container covered in this blog, I'll provide both Docker and Kubernetes options, being Docker the easy to begin with:
Docker (docker-compose)
If you're using Docker, drop this docker-compose.yml into a folder and run docker compose up -d. Adjust ports or restart policy as you like.
version: '3.9'
services:
it-tools:
image: 'corentinth/it-tools:latest'
ports:
- '8080:80'
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: it-toolsCommands:
Useful commands related with the docker compose method:
| Goal | Command |
|---|---|
| Start | docker compose up -d |
| Stop & remove | docker compose down |
| Remove preovious docker-run | docker container stop it-tools && docker container rm it-tools |
Open http://localhost:9080
Kubernetes (Deployment + NodePort)
This is a minimal single-node example (works well on K3s). For anything more durable, use a PVC and expose the app via an Ingress.
Save the Deployment as it-tools-deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: it-tools-deployment
labels:
app: it-tools
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: it-tools
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: it-tools
spec:
containers:
- name: it-tools
image: corentinth/it-tools:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "128Mi"
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "256Mi"
Save the Service as it-tools-service-nodeport.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: it-tools-service-nodeport
labels:
app: it-tools
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: it-tools
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 31080
Apply and check:
kubectl apply -f it-tools-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f it-tools-service-nodeport.yaml
kubectl get pods -l app=it-tools
kubectl get svc it-tools-service-nodeport
Open: http://:<node_ip>:31080
Notes:
- Prefer exposing via an Ingress and using cert-manager for TLS rather than NodePort for public-facing services.
Some Tools Examples
I'll give some examples of the tools you can find, but remember there's much more!
When loading the web application, it should look as follows:

There you can find each available tool. You can also use the search bar on top, or the navigation menu on the left, which is grouped by utilities.
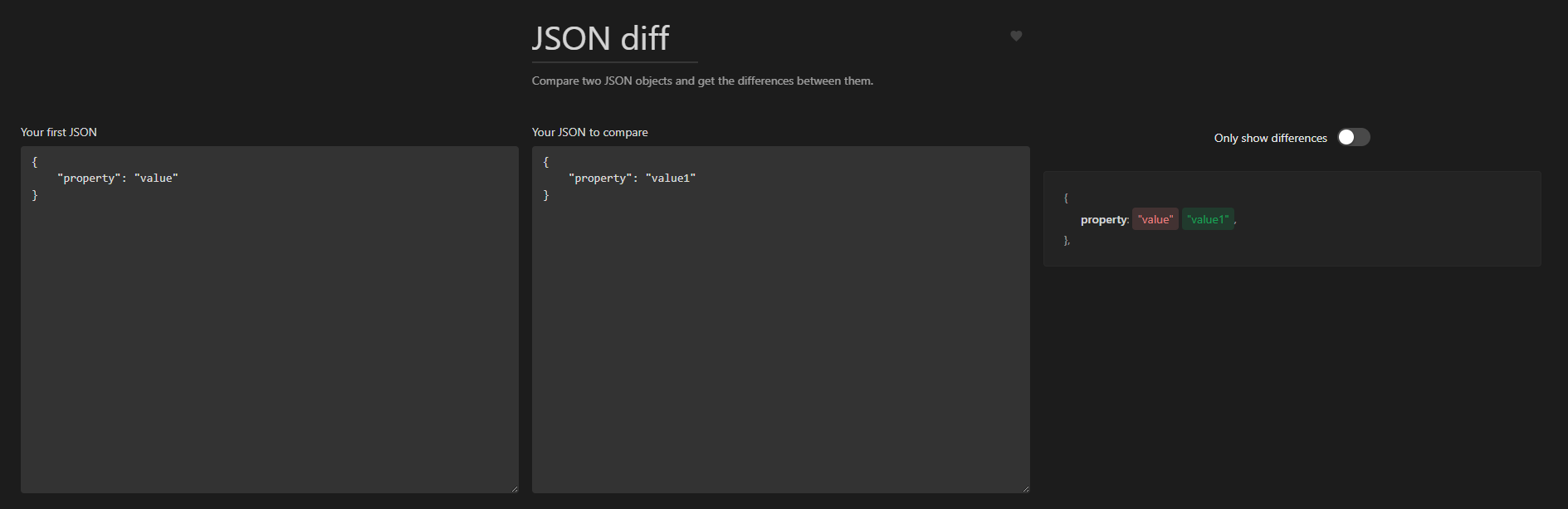
JSON Diff
Useful when comparing JSON files searching for differences:
Docker Run to Docker Compose
Pretty handy when you just want a docker-compose.yml file from a docker container run command you just executed. I've used IT Tools own command as example:

Note that it warns us about not translatable options!
JSON to YAML Converter
Save us some time when changin JSON files to YAML, just paste the JSON on the left and let IT Tools do all the work.

This converters has their counterparts, in this case, the YAML to JSON converter:

Uninstall / cleanup
Follow this steps if you want to remove IT Tools:
Docker:
- If you used
docker run:
docker container stop it-tools
docker container rm it-tools
- If you used
docker compose:
docker compose down
Kubernetes:
kubectl delete -f it-tools-service-nodeport.yaml -f it-tools-deployment.yaml
# Remove any hostPath data if you used it manually:
# sudo rm -rf /data/it-tools
Wrap-up
IT Tools is a practical collection of features that help us in a daily basis. Start with the Docker installation method if you want the fastest way, or use Kubernetes for robustness. I hope you found this useful!
